Heater Cartridges: Probably More Than You Wanted To Know About
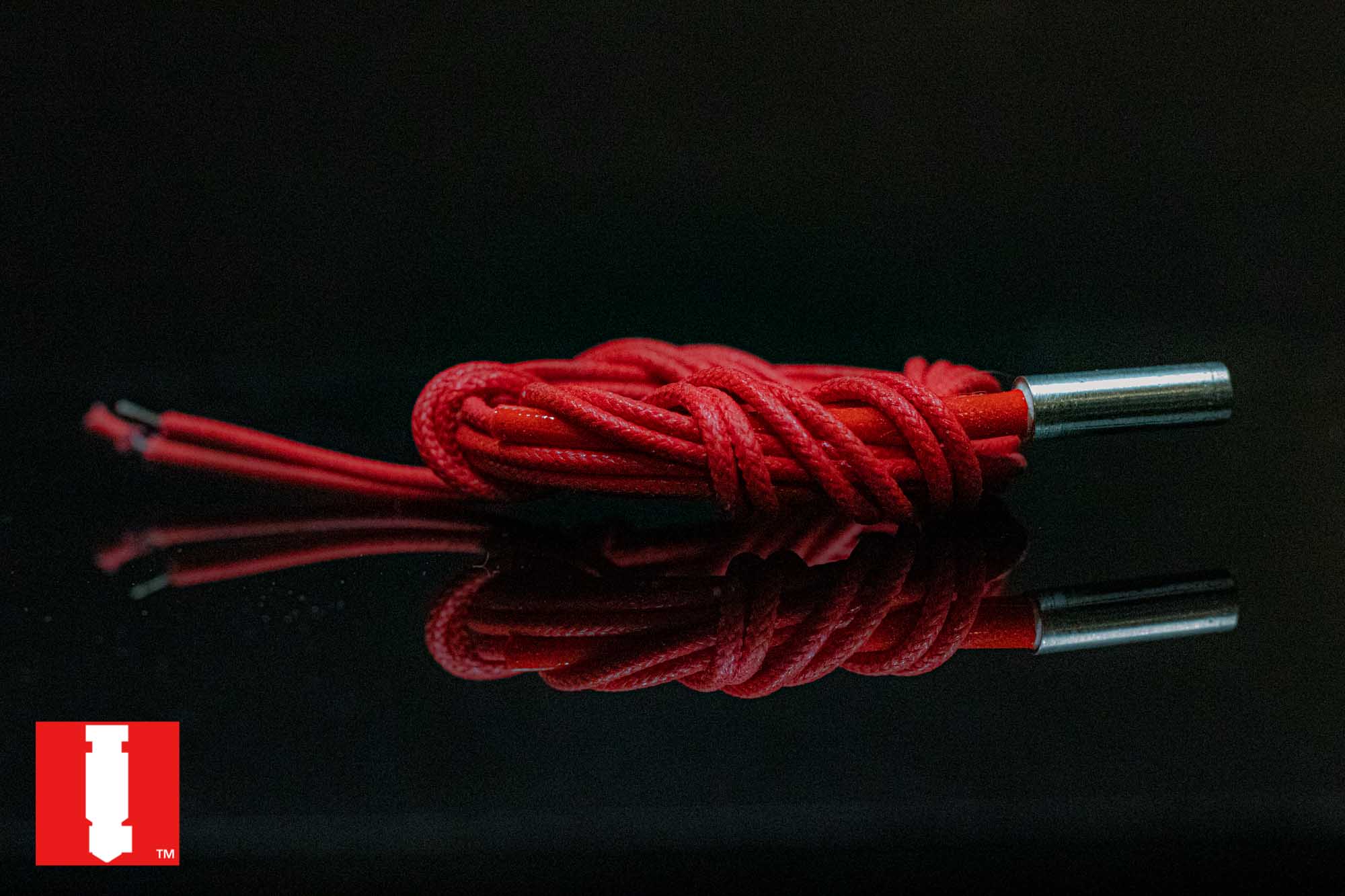

Are you looking for a reliable and comprehensive guide on how to choose the right heater cartridge for your 3D printer hotend? Look no further! In this article, we'll provide you with everything you need to know about heater cartridges, including what they are, how they work, and what wattage and voltage ratings to consider when purchasing one.
What is a heater cartridge?
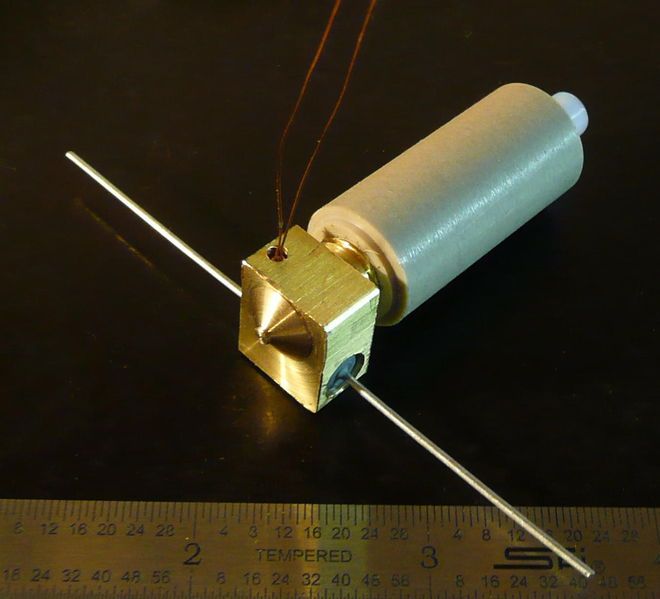
A heater cartridge is a tube-shaped resistive heating element that converts electricity into heat. In 3D printers, we use heater cartridges to melt plastic filament in the hotend.
How do heater cartridges work?
Heater cartridges are the workhorses of 3D printing. They're simple but effective devices that generate heat by converting electrical energy into thermal energy. When electric current flows through the cartridge, its resistance causes a buildup of energy that's released as heat. The higher the resistance, the more heat is produced. Conversely, the lower the resistance, the less heat is generated.
But how do we control the temperature of these heating elements? That's where thermistors come in. These are sensors that detect changes in temperature and alter the resistance of the cartridge accordingly. As the temperature rises, the resistance of the thermistor decreases, allowing more current to flow through the cartridge and generate more heat. This feedback loop is essential for maintaining a steady and precise temperature, which is critical for 3D printing.
Of course, all of this would be for naught if we didn't have a way to turn the heater on and off as needed. That's where the control board comes in. This circuit board is responsible for managing the various components of the printer, including the heater cartridge. By sending electrical signals to the cartridge, it can regulate the amount of heat being produced and maintain the desired temperature throughout the printing process.
In summary, heater cartridges are simple but powerful devices that convert electrical energy into thermal energy, allowing us to create objects layer by layer. With the help of thermistors and a control board, we can precisely control the temperature of these elements and produce high-quality prints.
What should you consider when choosing a heater cartridge?
Before looking at wattage, it is helpful to understand where that number comes from. When selecting a heater cartridge for your 3D printer, there are several factors to consider. One important factor is the wattage of the cartridge, which determines how quickly it can heat up and maintain temperature.
Wattage is calculated using Ohm's law, which states that:
voltage (V) equals current (I) multiplied by resistance (R), or V = IR.
It's also important to note that higher wattage heater cartridges can sometimes overshoot the desired temperature, resulting in the need for additional tuning and calibration. On the other hand, a lower wattage cartridge may offer more precise temperature control, particularly in situations where a specific temperature range must be maintained. Additionally, using a lower wattage cartridge can also extend the lifespan of your heating element, as it will experience less wear and tear over time. Ultimately, the wattage of your heater cartridge should be chosen based on your specific printing needs and preferences.
Heater Cartridge Wattage Calculator
Looking for more great calculators? Head on over to the 3D Printer Calculators page for all your calculating needs!
In addition to wattage, you'll also need to consider the voltage rating of the cartridge, which is typically 12V or 24V for most 3D printers. The voltage and resistance of the cartridge can be used to calculate the current required to achieve a specific power output using the formula I = P/V or I = sqrt(P/R).
By understanding these factors and using Ohm's law to calculate the appropriate wattage and current for your heater cartridge, you can ensure that your 3D printing setup operates efficiently and effectively.
So what wattage do you need?
Printing with fiber-reinforced PEEK typically requires high temperatures, with extrusion temperatures ranging from 360°C to 420°C (680°F to 788°F)
When it comes to choosing the right wattage for your 3D printing heater cartridge, there are a few things to consider. First, you'll want to think about what materials you plan to print with and at what temperatures. Different materials require different temperatures, so you'll need to make sure that your heater cartridge is capable of reaching the necessary temperatures.
In general, heater cartridges with wattage ratings of 20W or less may not provide enough power for 3D printing, especially if you plan to print with materials that require high temperatures. On the other hand, cartridges with wattage ratings of 60W or higher are typically used for specialized applications and may not be necessary for most hobbyist 3D printing setups.
For most 3D printing enthusiasts, a 30W heater cartridge is a great option. It provides a good balance between performance and safety and is capable of heating up to around 300°C (572°F), which is sufficient for printing most standard plastics. If you need to print with high-temperature materials, such as carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK, a 30W cartridge with an insulating silicone sock around the hotend can reach temperatures of up to 420°C (788°F).
It's important to note that higher wattage heater cartridges can consume more power and may require a more powerful power supply, which can increase the cost of your setup. Additionally, using a higher wattage cartridge may put more strain on your printer's components and could result in reduced lifespan. So, while higher wattage cartridges may seem tempting for faster heat-up times, it's best to consider your specific needs and choose a wattage that meets those needs without going overboard.
Matching the Rated Voltage of Your Heater Cartridge
In addition to choosing the right wattage for your heater cartridge, it's also important to ensure that the rated voltage of your cartridge matches that of your 3D printer power supply output voltage.
Most 3D printers run on either 12V or 24V, so choosing a heater cartridge with the corresponding voltage rating is important. If the voltage rating of your heater cartridge does not match that of your power supply, it can lead to issues with heating and potentially damage your hotend or other components.
When using a heater cartridge, it's important to make sure it's compatible with the power supply you're using. If you connect a heater cartridge with the wrong voltage, it can have disastrous consequences.
For example, let's say you have a 12v 40W heater cartridge with a resistance of 3.6 Ω. If you connect it to a 12V power supply, you'll get the full 40W of power output (P = V^2/R = 12^2/3.6 = 40W). However, if you connect the same 12v 40W heater cartridge to a 24V power supply, you'll get a whopping 160W of power output (P = V^2 / R = 24^2 / 3.6 = 160W).
On the other hand, a 24V 40W heater cartridge typically has a resistance of around 14.4 Ω. If you connect it to a 24V power supply, you'll get the full 40W of power output (P = V^2/R = 24^2/14.4 = 40W). However, if you connect the same 24V 40W heater cartridge to a 12V power supply, you'll only get about 10W of power output (P = V^2/R = 12^2/14.4 = 10W). This surely will not be enough to reach the desired temperature for your printing needs.
To avoid these problems, always make sure the voltage rating of your heater cartridge matches that of your power supply.
Why Don't We Use Nichrome Anymore?
In 2011, when the RepRap movement was still in its infancy, many 3D printing enthusiasts were still using hand-made hotends with wrapped nichrome wire heaters. However, around this time, a new hotend called J-Head™ started producing commercial hotends that utilized power resistors instead of nichrome wire. This was a major breakthrough in the industry, as it simplified the process of creating hotends and made them more accessible to the average user.
The J-Head™ hotend was particularly popular among DIY 3D printing enthusiasts. When heater cartridges entered the scene J-Head™ owners were able to swap out their power resistors for the newer heater cartridges since they had a similar diameter. This allowed users to take advantage of the simplified design of the J-Head™ hotend without having to replace the entire unit!
Overall, the introduction of power resistors in hotends like the J-Head™ marked a significant step forward in the development of 3D printing technology and helped pave the way for the more advanced and user-friendly hotends we see on the market today.
 Proudly Made In The USA
Proudly Made In The USA
Patel Heaters and Control Pvt Ltd
says:Keep sharing this wonderful blog related to Cartridge Heater, which tells its meaning, working & vital role in the heating industry. I really like your writing skills. Keep sharing, I’m waiting for more blogs!